Challenges and Future Directions in Intrathecal Therapy
Intrathecal therapy has revolutionized the treatment of central nervous system (CNS) disorders. By delivering medication directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, this method bypasses the blood-brain barrier, offering a targeted approach. However, despite its advantages, intrathecal therapy encounters significant challenges. These include limited drug options and associated risks. Addressing these issues is essential to improve patient outcomes. This blog delves into these challenges and explores potential future directions to enhance the efficacy and safety of intrathecal drug delivery.
Understanding Intrathecal Therapy
What Is Intrathecal Drug Delivery?
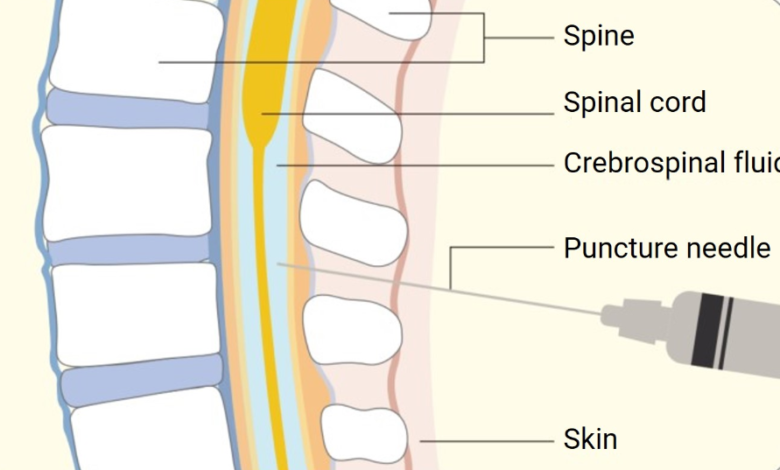
Intrathecal drug delivery involves administering medication directly into the spinal canal’s cerebrospinal fluid. This method ensures that drugs reach the CNS, which is otherwise difficult due to the protective blood-brain barrier. It is primarily used for pain management and spasticity control.
Why Is Intrathecal Therapy Used in CNS Treatment?
Intrathecal therapy is preferred for its precision in targeting CNS disorders. It allows lower doses of drugs with fewer systemic side effects. Conditions such as chronic pain, spasticity from multiple sclerosis, and severe cancer pain benefit significantly from this localized delivery system.
See also: How Exercise Impacts Liver Health: Benefits and Guidelines
Key Challenges in Intrathecal Therapy
Limited Drug Delivery Options
The blood-brain barrier, designed to protect the brain, significantly limits the number of drugs that can effectively treat CNS conditions. While intrathecal therapy circumvents this barrier, it currently accommodates only a limited range of drugs. This limitation often necessitates off-label use, which can be risky. The development of new drugs suitable for intrathecal delivery is slow, further constraining treatment options for patients with complex CNS disorders. Additionally, the formulation of these drugs must ensure stability and effectiveness once administered, posing another layer of complexity.
Risks and Complications of Intrathecal Administration
Although beneficial, intrathecal therapy is not without risks. Infection is a major concern, as the invasive technique of inserting catheters or pumps introduces potential pathways for pathogens. Device malfunction or dislodgement can lead to uneven drug distribution, causing fluctuations in therapeutic efficacy and possibly leading to overdose or underdose. Additionally, patients might experience complications such as bleeding, cerebrospinal fluid leaks, or nerve damage during insertion or maintenance of intrathecal devices. These challenges necessitate rigorous procedural standards and comprehensive patient monitoring.
Overcoming the Current Limitations
Technological Innovations in Intrathecal Drug Delivery
Innovative technologies are essential to overcoming the current limitations in intrathecal therapy. Advances such as programmable pumps allow for precise drug dosages, enhancing treatment accuracy. Additionally, research into biodegradable polymers for drug delivery systems shows promise. These polymers can provide sustained release of medication, reducing the need for frequent interventions and minimizing infection risks. The integration of smart technology in these devices is likely to further improve clinical outcomes and patient safety.
Improving Patient Safety in Intrathecal Procedures
Patient safety is paramount in the administration of intrathecal therapy. Implementing stringent aseptic techniques during catheter insertion and maintenance can significantly reduce infection risks. Training healthcare professionals in the latest procedural advancements ensures that potential complications are minimized. Regular monitoring and follow-up with patients are also essential to promptly identify and address any adverse effects. Research on new materials for catheters and pumps that reduce the risk of dislodgement and malfunction is ongoing, contributing to safer and more reliable intrathecal treatments.
Future Directions in Intrathecal Therapy
Advancements in Drug Formulations for Intrathecal Use
The future of intrathecal therapy hinges on developing advanced drug formulations. Scientists are exploring novel molecules and biological agents specifically tailored for intrathecal administration. These innovations promise more effective treatments for complex CNS disorders. Enhanced formulations with extended-release capabilities can streamline treatment, reducing the frequency of interventions and improving patient compliance.

Personalized Medicine and Intrathecal Delivery Systems
Personalized medicine represents the next frontier in intrathecal therapy. Tailoring treatment plans to individual patient profiles can maximize therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects. Advanced diagnostics and biomarkers will play a crucial role in customizing intrathecal drug delivery. This individualized approach not only optimizes outcomes but also fosters a proactive stance in managing CNS conditions, paving the way for more dynamic and responsive treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Intrathecal therapy stands as a pivotal approach in treating CNS disorders, yet it comes with significant challenges. By addressing drug limitations and minimizing procedural risks through technological and procedural advancements, we can enhance this crucial therapy. Looking forward, the synergy of advanced drug formulations and personalized medicine promises to elevate the standard of care in intrathecal treatments, ultimately offering patients a better quality of life.